Detection of fake accounts promoting Cyber threats using Machine Learning Methods
Keywords:
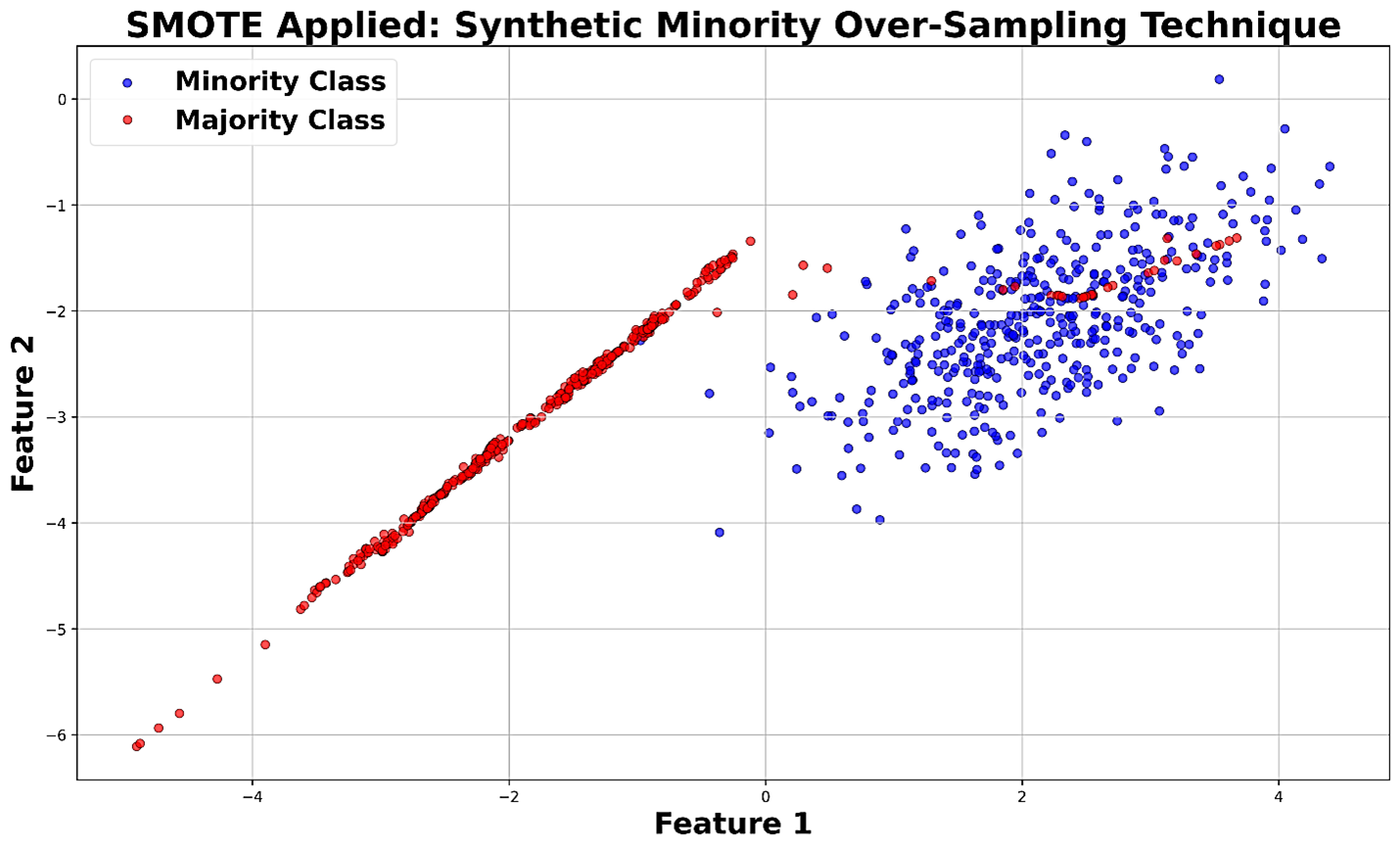
Fake account detection, cyber threats, metadata analysis, behavioral features, supervised machine learning, Random Forest, real time inference, SMOTE, ethical AIAbstract
A large number of fake online accounts creates difficulties for cybersecurity, since the owners of these accounts can share lies, plan assaults and boost cyber problems. In our research, we apply a strictly bounded approach that makes use of machine learning to identify fake accounts using their associated noncontent features. We built a database with 10,000 accounts (half of which were fake, half genuine) taken from (Twitter/X, Instagram) and then looked at nine main features such as account age, the relationship between followers and people the account follows, how often posts are made, how long each post’s gap is, average session duration, the spread of IP addresses, the number of different devices used and fast switching of IP addresses. After the data was cleaned, normalized and data imbalances were corrected with SMOTE if the ratio was higher than 1.5 to 1, a hyperparameters optimized Random Forest classifier with 100 trees were tuned using 5-fold cross validation. For the fake account class, the model got 91.0 % accuracy, 93.4 % precision, 89.2 % recall and a 91.3 % F₁ score using the 3,000 hold out test set. Performing learning curves and permutation tests, we confirmed that the highlights of the project were reliable and significant. Testing on 1,000 new account profiles revealed that it took less than ten milliseconds to infer connections for each account (performing as expected for 94 % of cases). Using public data restriction, approval from an ethics board, keeping logs for a short period and being transparent help to use AI responsibly. Based on our findings, Metadata classifiers can effectively and fast stop attacks caused by fake accounts.