Toward Improved ICU Care - Phlebotomy Frequency Using Deep Learning
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.65718/Keywords:
Intensive Care Unit, ICU, Iatrogenic Anemia, Long-Short-Term Memory, LSTM, Phlebotomy Frequency Prediction, Variable Multi-Output SequenceAbstract
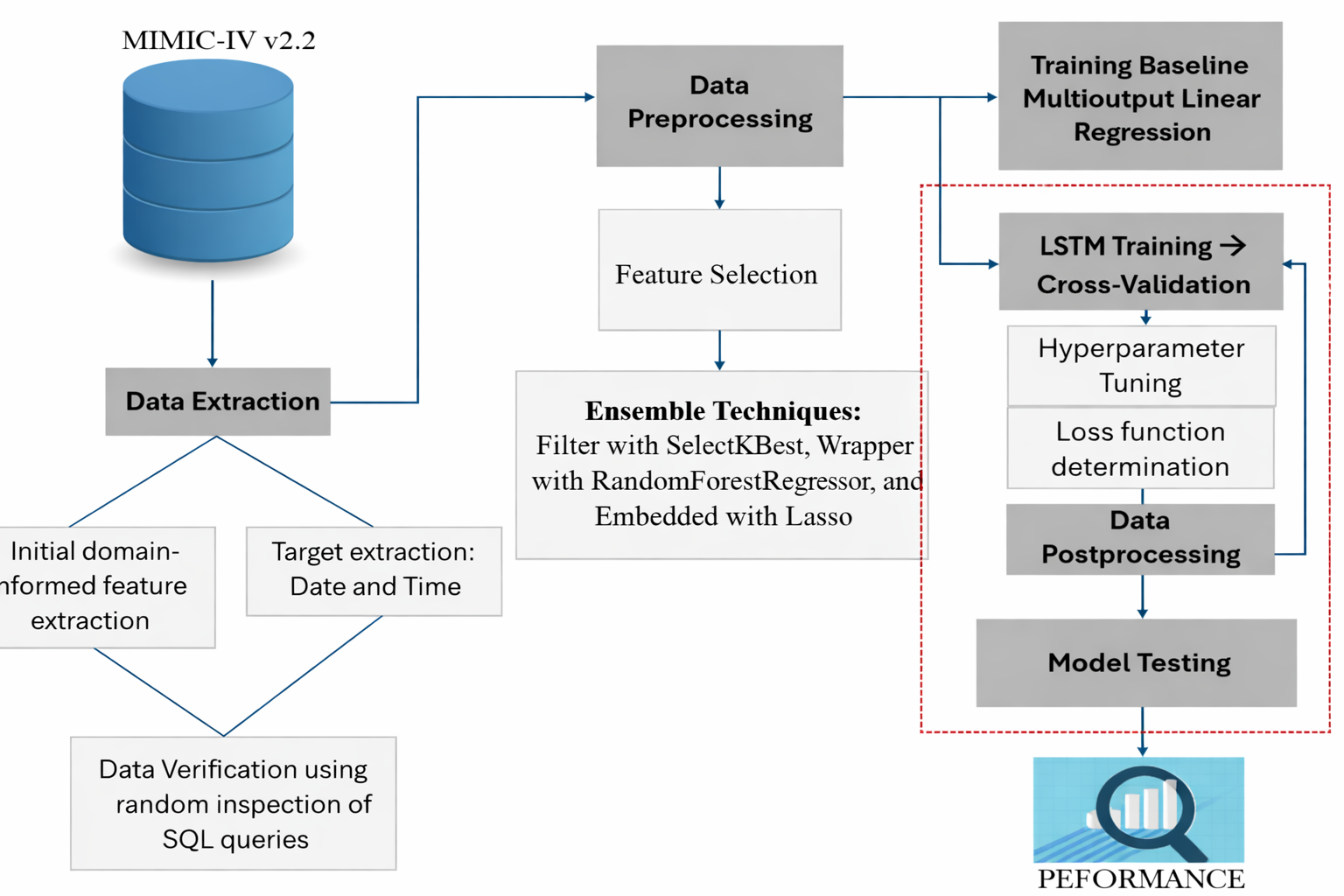
Frequent phlebotomies in Intensive Care Units (ICUs) are crucial for patient monitoring but pose significant challenges, including complications such as iatrogenic anemia, which affects up to 70% of ICU patients. Traditional blood sampling methods do not sufficiently mitigate anemia or improve blood draw frequency. Recent advancements in Artificial Intelligence (AI) offer promising opportunities to enhance healthcare practices in the ICU, especially by analyzing diverse patient data, such as vital signs, blood test results, and demographics. However, existing AI models have predominantly focused on predicting isolated blood test results, rather than providing a holistic solution to forecast blood draw needs throughout a patient's ICU stay. This study addresses this gap by developing a Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) model to predict blood draw frequency upon ICU admission, using key temporal, quantitative, and patient-specific features. Trained on data extracted from a real-world database, the model demonstrates promising performance, particularly by incorporating a novel loss function in the field to improve predictions of variable multi-output sequence lengths. This research introduces the first predictive model for ICU blood draw frequency, shifting the approach from reactive to proactive care. It underscores the potential of AI to personalize ICU practices, reduce unnecessary blood draws, and improve patient outcomes.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2026 Inspire Intelligence

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.



