Interpretable Deep Learning for Breast Lesion Classification: A SHAP-Based Comparison of CESM and Digital Mammography
Keywords:
Breast cancer, Convolutional neural network, SHAP, Digital mammography, Contrast-enhanced spectral mammographyAbstract
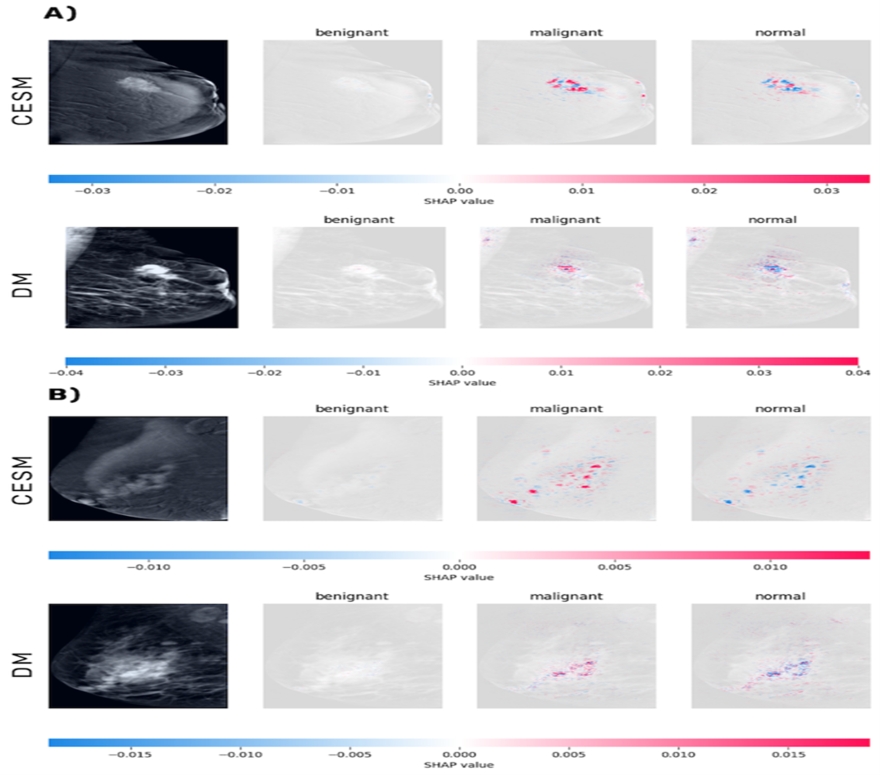
Accurate detection of malignant breast lesions is fundamental for timely intervention and improved patient outcomes. Digital Mammography (DM) remains the standard imaging modality in most clinical settings. In contrast, Contrast-Enhanced Spectral Mammography (CESM) provides functional imaging data, which has the potential to improve the performance of deep learning algorithms in lesion detection. Materials and Methods: The study compares a ResNet-18 CNN trained on DM versus CESM for breast-lesion classification, uses 80% stratified 3-fold cross-validation, evaluates the best model on a held-out 20% blind test, and assesses interpretability with SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP) attribution maps. Results: On the blind test set, CESM achieved superior overall classification performance, with an AUC of 0.890 for malignant lesions compared to 0.790 for DM. The micro- and macro-averaged AUCs are 0.83 and 0.77 for CESM, respectively, compared to 0.68 and 0.68 for DM. SHAP analysis revealed that CESM yielded more focused and anatomically aligned model attributions, particularly in malignant cases. DM produced more diffuse, yet still lesion-centered, attribution patterns. Conclusion: CESM substantially improves CNN-based diagnostic accuracy and interpretability in breast lesion classification, with the most significant benefit observed in the detection of malignant lesions, which is the most clinically significant category. Although it is still challenging to classify benign lesions, DM can help identify malignancies without the need for contrast, making it useful for screening when CESM is not available. These results show the value of CESM-enhanced Artificial Intelligence (AI) systems and explainability tools for dependable use in clinics.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2026 Inspire Intelligence

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.



